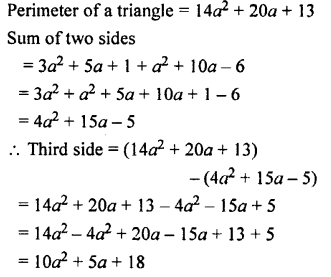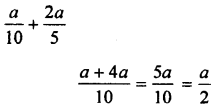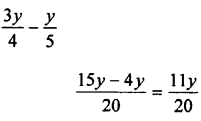Parents can use OP Malhotra Maths Class 11 Solutions Chapter 9 Complex Numbers Ex 9(c) to provide additional support to their children.
S Chand Class 11 ICSE Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Complex Numbers Ex 9(c)
Question 1.
If (- 2 + \(\sqrt{-3}\)) (- 3 + 2\(\sqrt{-3}\)) = a + bi, find the real numbers a and b with values of a and b, also find the modulus of a + bi.
Solution:
(- 2 + \(\sqrt{-3}\)) (- 3 + 2\(\sqrt{-3}\)) = a + bi
⇒ (- 2 + \(\sqrt{-3}\)i)(- 3 + 2\(\sqrt{-3}\)i) = a + ib
⇒ 6 – 4\(\sqrt{-3}\)i – 3\(\sqrt{-3}\)i – 6 = a + ib
⇒ – 7\(\sqrt{-3}\)i = a + ib
On comparing real and imaginary parts on both sides, we get
a = 0 ; b = – 7\(\sqrt{-3}\)
∴ |a + ib | = |0 + (- 7\(\sqrt{-3}\))i| = 7\(\sqrt{-3}\)
Question 2.
Find the modulus of (1 – i)-2 + (1 + i)-2.
Solution:
(1 – i)-2 + (1 + i)-2 = \(\frac{1}{(1-i)^2}+\frac{1}{(1+i)^2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{1-1-2 i}+\frac{1}{1-1+2 i}\)
= \(\frac{-1}{2 i}+\frac{1}{2 i}\) = 0
∴ |1(1 – i)-2 + (1 + i)-2| = |0| = o
![]()
Question 3.
If z = 6 + 8i, verify that
(i) | z | = | \(\bar { z }\) |
(ii) – | z | < Re (z) ≤ | z |
(iii) – | z | < Im (z) ≤ | z |
(iv) z-1 = \(\frac{\bar{z}}{|z|^2}\)
Solution:
Given z = 6 + 8i ∴ \(\bar { z }\) = \(\overline{6+8 i}\) = 6 – 8i
(i) | z | = 6 + 8i = \(\sqrt{6^2+8^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{36+64}=\sqrt{100}\) = 10
|z| = |6 – 8i| = \(\sqrt{6^2+(-8)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{36+64}=\sqrt{100}\) = 10
∴ |z| = |\(\bar { z }\)|
(ii) since – 10 ≤ 8 ≤ 10
⇒ – | z | ≤ Re (z) ≤ | z |
(iii) since – 10 ≤ 8 ≤ 10
⇒ – | z | ≤ Im (z) ≤ | z |
(iv) z-1 = (6 + 8i)-1 = \(\frac{1}{6+8 i} \times \frac{6-8 i}{6-8 i}\)
= \(\frac{6-8 i}{36+64}=\frac{6-8 i}{100}\)
and \(\frac{\bar{z}}{|z|^2}=\frac{6-8 i}{\left[\sqrt{6^2+8^2}\right]^2}=\frac{6-8 i}{100}\)
∴ z-1 = \(\frac{\bar{z}}{|z|^2}\)
Question 4.
If z1 = 3 + 4i, z2 = 8 – 15i, verify that
(i) | – z1| = | z1|
(ii) | z²1| = |z1|²
(iii) |z1z2| = |z1| |z2|
(iv) \(\left|\frac{z_1}{z_2}\right|=\frac{\left|z_1\right|}{\left|z_2\right|}\)
(v) | z1| + z2| < | z1| + | z2 |
(vi) | z2 – z1 | > \(|| z_2|-| z_1||\)
(vii) |z1 + z2|² + |z1 – z2|² = 2(|z1|² + | z2|²).
Solution:
z1 = 3 + 4i; z2 = 8 – 15i
(i) – z1 = – (3 + 4i) = – 3 – 4i
∴ |- z1 | = \(\sqrt{(-3)^2+(-4)^2}=\sqrt{9+16}\) = 5
| z, | = \(\sqrt{3^2+4^2}=\sqrt{9+16}=\sqrt{25}\) = 5
∴ |- z1 | = | z1|
(ii) z1² = (3 + 4i)² = 9 – 16 + 24i
= – 7 + 24i
∴ \(\left|z_1^2\right|=\sqrt{(-7)^2+24^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{49+576}=\sqrt{625}\) = 25
|z1|² = \(\left(\sqrt{3^2+4^2}\right)^2\)
= 9 + 16 = 25
∴ \(\left|z_1^2\right|=\left|z_1\right|^2\)
![]()
(iii) z1z2 = (3 + 4i) (8 – 15i)
= 24 – 45i + 32i + 60
⇒ z1z2 = 84 – 13i
∴ |z1z2| = \(\sqrt{84^2+(-13)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{7056+169}=\sqrt{7225}\) = 85
Here, | z1 | | z2 | = | 3 + 4i | | 8 – 15i |
= \(\sqrt{3^2+4^2} \sqrt{8^2+(-15)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{9+16} \sqrt{64+225}\)
= \(\sqrt{25} \sqrt{289}\) = 5 x 17 = 85
∴ \(\left|z_1 z_2\right|=\left|z_1\right|\left|z_2\right|\)

(vi) |z2 – z1 | = | 8 – 15i – 3 – 4i | = | 5 – 19i |
= \(\sqrt{5^2+(-19)^2}=\sqrt{25+361}\)
= \(\sqrt{386}\) … (1)
\(|| z_2|-| z_1||=\left|\sqrt{8^2+(-15)^2}-\sqrt{3^2+4^2}\right|\)
= | 17 – 5 | = 12
From (1) and (2); we have
\(\left|z_2-z_1\right|>|| z_2|-| z_1||\) [∵ \(\sqrt{386}\) > 12]
(vii) z1 + z2 = 3 + 4i + 8 – 15i = 11 – 11i
and z1 – z2 = 3 + 4i – 8 + 15i = – 5 + 19i
L.H.S = | z1 + z2|² + | z1 – z2|
= | 11 – 11i |² + | – 5 + 19i |²
= \(\left(\sqrt{11^2+(-11)^2}\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{(-5)^2+19^2}\right)^2\)
= \((\sqrt{121+121})^2+(\sqrt{25+361})^2\)
= \((11 \sqrt{2})^2+(\sqrt{386})^2\)
= 242 + 386 = 628
R.H.S = 2\(\left(\left|z_1\right|^2+\left|z_2\right|^2\right)\)
= 2 \(\left(\left(\sqrt{3^2+4^2}\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{8^2+(-15)^2}\right)^2\right)\)
= 2 (25 + 289) = 2 x314 = 628
∴ L.H.S = R.H.S.
Question 5.
Find the modulus of the following using the property of modulus.
(i) (3 + 4i) (8 – 6i)
(ii) \(\frac{8+15 i}{8-6 i}\)
(iii) \(\frac{3+2 i}{2-5 i}+\frac{3-2 i}{2+5 i}\)
(iv) \(\frac{(2-3 i)(4+5 i)}{(1-4 i)(2-i)}\)
Solution:
(i) Let z = (3 + 4i) (8 – 6i)
∴ | z | = |(3 + 4i)(8 – 6i)|
= | 3 + 4i | | 8 – 6i | [∵ |z1z2 | = | z1 | | z2 |]
= \(\sqrt{3^2+4^2} \sqrt{8^2+(-6)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{9+16} \sqrt{64+36}\) = 5 x 10 = 50
(ii) Let z = \(\frac{8+15 i}{8-6 i}\)

Question 6.
Let z be a complex number such that \(\left|\frac{z-5 i}{z+5 i}\right|\) = 1, then show that z is purely real.
Solution:
Let z = x + iy

On squaring both sides, we have
x² + (y – 5)² = x² + (y + 5)²
⇒ x² + y² + 25 – 10y = x² + y² + 25 + 10y
⇒ 20y = 0
⇒ y = 0
∴ z = x, which is purely real.
Question 7.
Find the complex number z satisfying the equation \(\left|\frac{z-12}{z-8 i}\right|=\frac{5}{3},\left|\frac{z-4}{z-8}\right|\) = 1.
Solution:
Let z = x + iy
Given \(\left|\frac{z-12}{z-8 i}\right|=\frac{5}{3}\) ⇒ \(\left|\frac{x+i y-12}{x+i y-8 i}\right|=\frac{5}{3}\)
⇒ \(\frac{|(x-12)+i y|}{|x+i(y-8)|}=\frac{5}{3}\) [∵ \(\left|\frac{z_1}{z_2}\right|=\frac{\left|z_1\right|}{\left|z_2\right|}\) ]
\(\frac{\sqrt{(x-12)^2+y^2}}{\sqrt{x^2+(y-8)^2}}=\frac{5}{3}\)
On squaring both sides ; we have
⇒ \(\frac{(x-12)^2+y^2}{x^2+(y-8)^2}=\frac{25}{9}\)
⇒ 9 [(x- 12)² + y²] = 25 [x² + (y – 8)²]
⇒ 9 [x² – 24x + 144 + y²] = 25 [x² + y² – 16y + 64]
⇒ 16 (x² + y²) – 400y + 216x + 304 = 0
⇒ 2x² + 2y² – 50y + 27x + 38 = 0 …(1)
Also, \(\left|\frac{z-4}{z-8}\right|\) = 1 ⇒ \(\left|\frac{x-4+i y}{x-8+i y}\right|\) = 1
⇒ \(\sqrt{(x-4)^2+y^2}=\sqrt{(x-8)^2+y^2}\)
On squaring both sides ; we have
(x – 4)² + y² = (x – 8)² + y²
⇒ x² – 8x + 16 = x² – 16x + 64
⇒ 8x – 48 = 0
⇒ x = 6
∴ from (1); we have
2 x 6² + 2y² – 50y + 27 x 6 + 38 = 0
⇒ 72 + 2y² – 50y + 162 + 38 = 0
⇒ 2y² – 50y + 272 = 0
⇒ y² – 25y + 136 = 0
∴ y = \(\frac{25 \pm \sqrt{625-544}}{2}=\frac{25 \pm 9}{2}\)
⇒ y = 17, 8
Thus required complex numbers are 6 + 17i and 6 + 8i.
![]()
Question 8.
If z is a complex number such that
| z – 1 | = | z + 1|, show that Re (z) = 0.
Solution:
Given |z – 1 | = |z + 1|; where z = x + iy
⇒ |x + iy – 1 | = |x + iy + 1|
⇒ |(x – 1) + zy | = |(x + 1) + iy |
⇒ \(\sqrt{(x-1)^2+y^2}=\sqrt{(x+1)^2+y^2}\)
On squaring both sides ; we have
(x – 1)² + y² = (x + 1)² + y²
⇒ x² – 2x + 1 = x² + 2x + 1
⇒ 4x = 0
⇒ x = 0
⇒ Re (z) = 0
Question 9.
Solve: | z | + z = 2 + i, where z is a complex number.
Solution:
Given | z | + z = 2 + i; where z = x + iy
⇒ \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\) + x + iy = 2 + i
Comparing real and imaginary parts on both sides ; we have
\(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\) + x = 2 …(1)
and y = 1 … (2)
∴ from (1) and (2); we have
\(\sqrt{x^2+1}\) = 2 – x ;
on squaring both sides, we have
⇒ x² + 1 = (2 – x)²
⇒ x² + 1 = 4 + x² – 4x
⇒ 3 – 4x = 0 ⇒ x = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
∴ required complex number z = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) + 1