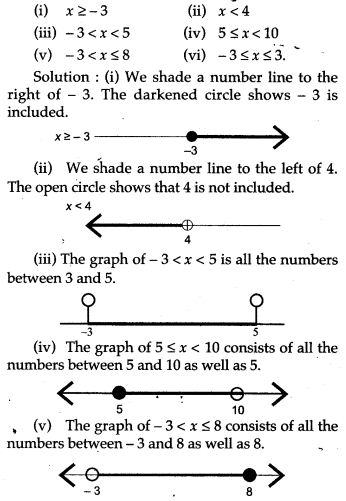
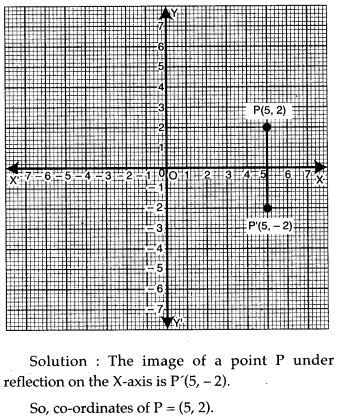
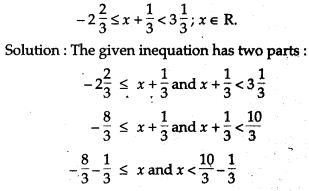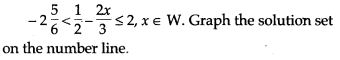APlusTopper.com provides ICSE Class 10 Home Science Previous Year Board Question Papers Solved Pdf Free Download with Solutions, Answers and Marking Scheme. Here we have given ICSE Class 10 Home Science Solved Question Papers Last Ten Years. Students can view or download the ICSE Board 10th Home Science Previous Year Question Papers with Solutions for their upcoming examination.
These ICSE Class 10 Home Science Previous 10 Years Board Question Papers with Answers are useful to understand the pattern of questions asked in the board exam. Know about the important concepts to be prepared for ICSE Class 10 Board Exam and Score More marks.
Board – Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE), www.cisce.org
Class – Class 10
Subject – Home Science
Year of Examination – 2020, 2019, 2018, 2017.
ICSE Class 10 Home Science Solved Question Papers Last Ten Years
- ICSE Home Science Question Paper 2019 Solved
- ICSE Home Science Question Paper 2018 Solved
- ICSE Home Science Question Paper 2017 Solved
- ICSE Home Science Question Paper 2016 Solved
- ICSE Home Science Question Paper 2015 Solved
- ICSE Home Science Question Paper 2014 Solved
We hope the ICSE Class 10 Home Science Previous Years Question Papers Solved Last 10 Years Pdf Free Download with Solutions will help you. If you have any query regarding ICSE Class 10 Home Science Solved Question Papers Last Ten Years with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.